425-373-1416
Tendonitis
Tendons are tough yet flexible bands of fibrous tissue that connect muscles to bones. The muscles have the function to move the bones, facilitating movements like walking, jumping, or lifting. When a muscle contracts it exerts force on a bone to produce movement and the tendon transmits this muscular force. There are hundreds of small and large tendons in the body but a few have an increased tendency to be injured because they have an area of poor blood supply that leads to tissue damage and poor healing. These areas are sometimes referred to as watershed zones, indicating that the body has difficulty bringing nutrients and oxygen to the afflicted tendon. When the tendons become inflamed, the activity of pulling the muscles becomes irritating and painful. This is called tendonitis, which means inflammation of the tendon, and is usually caused by overuse. When people begin a new activity that they are not used to, or perform a new form of exercise, tendons may become irritated. This is particularly true in older age because the flexibility and elasticity of the tendons have decreased. Sometimes a bone spur might be an anatomical cause for tendonitis.
Symptoms of tendonitis:
• Tenderness of the tendon
Tenderness of the tendon
• Pain with movement of the muscle and tendon
Pain with movement of the muscle and tendon
• Swelling and inflammation of the tendon
Swelling and inflammation of the tendon
Some of the tendonitis cases seen most frequently include:
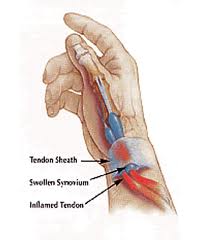
• Wrist tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis
This common form of tendonitis causes pain and swelling around the wrist,
usually the area around the thumb and anatomical snuff box. The area is usually
painful and inflamed and diagnosed with the Finkelstein’s test, where the patient
makes a fist that is then abducted towards the small finger side. Another name
for this tendonitis is DeQuervain’s tenosynovitis, so named for the thickening of
the synovium and tendon that controls movement of the thumb.
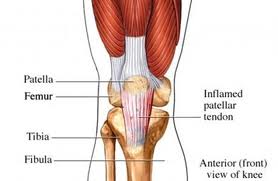
• Patellar tendonitis
Patellar tendonitis
Because it affects the tendon that connects the quadriceps muscles to the lower
leg, pain and swelling occurs in the inferior patellar region. It is common in athletes
and frequently referred to as jumper’s knee.
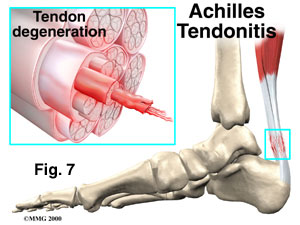
• Achilles tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis
The most common cause for Achilles tendonitis is insufficient stretching which causes a
lack of flexibility and excessive flexion of the foot. Other reasons include changes
in footwear, long distance running, running on an incline, or sudden, excessive
exercising (weekend warrior injury). As people age, their blood and fluid levels decline
and the tissues become more rigid and inflexible. Middle aged persons taking part in
recreational exercises are most prone to tendon injuries.
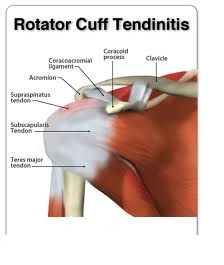
• Shoulder tendonitis
Shoulder tendonitis
Shoulder bursitis and rotator cuff tendonitis are different ways of saying there is
inflammation of a particular area within the shoulder joint that is causing a common set
of symptoms. The proper terminology for these symptoms is “impingement syndrome”.
Impingement syndrome occurs when there is inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons and
the bursa that surrounds these tendons. There is a difference between tendinitis and
bursitis, but in most cases of impingement syndrome there is a combination of these
problems.
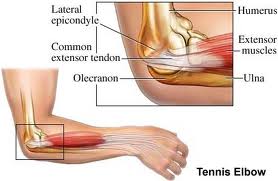
• Elbow tendonitis, tennis elbow, lateral epicondylitis
Elbow tendonitis, tennis elbow, lateral epicondylitis
These three terms can be used interchangeably for the symptoms of elbow pain, seen
at the insertion of the forearm and wrist extensor muscles into the humerus, near the elbow.
Tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis is the most common injury in patients seeking
TCM treatments for elbow pain. The cause of tennis elbow is thought to be due to small
tears of the tendons that attach the forearm muscles to the arm bone at the elbow joint.
Treatments with Chinese Medicine:
In Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), tendonitis is treated by the approach of activating Qi and Blood flow to nourish the tendons. As you already know, some tendons have very poor blood supply. As is understood by the tenets of TCM, energy is the leader of the blood. If energy circulation is poor, then blood circulation is poor as well. The two are mutually interdependent. As a consequence, the therapeutic approach is to both activate energy flow and increase the blood circulation. This can be done in various ways, including acupuncture to drive energy and blood to the tendons, Tui-na massage, heat therapy with moxibustion, some forms of cupping, and Chinese herbal formulas. If tendonitis is treated properly complete healing can be achieved, however the treatment of tendonitis requires a longer period of treatments than a muscular problem.